
- #Magic packet sender portable password
- #Magic packet sender portable Pc
- #Magic packet sender portable free
- #Magic packet sender portable mac
You can also use Tasker to issue the command to Raspberry PI as WOL. From the mobile, you could use a JuiceSSH app that lets you do the same thing but from the mobile. Here you have few choices, obviously, you can log into the terminal, and issue the command manually or run the script (which also needs a command). Each time we will try to communicate with your IP or DNS through the port 22, the router will send us to the Raspberry PI. You want to forward the port 22 to an IP that has been assigned to the WIFI interface. Log in to the router admin page (usually 196.168.1.0 or similar) and find the port forwarding settings. I will assume that you have not changed the SSH port number (22 by default). To get the information from the internet to your Raspberry, you have to tell the router which device you are trying to address.
#Magic packet sender portable Pc
Fear not, I already have a handy guide in here. Once you have the static IP with your router and the PC time to get the Raspberry PI visible outside of the network (skip this if you interested in WOL functionality over the local network only). First, we have to make sure the Raspberry PI has a static IP.
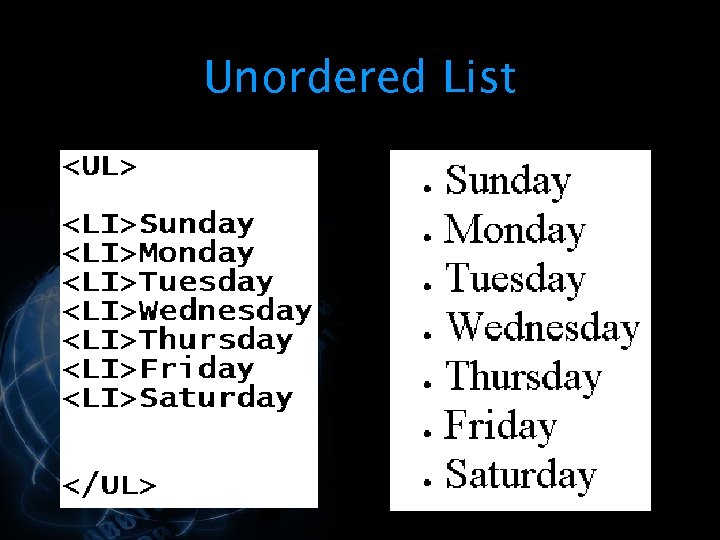
You can execute this line in the terminal, or use a simple bash script to open instead, that will do this for you #!/bin/bashĪnd save it as wol.sh then run it with sudo permissions: sudo bash /path/to/file/wol.sh Sending WOL command to the Raspberry PI as WOL The WOL packet will be sent as a broadcast to all devices on the network.
#Magic packet sender portable mac
The AA:BB:CC:DD:EE:FF is the MAC address of the device you want to wake up.
#Magic packet sender portable password
Send the wake-up packet to the broadcast address.Īppend a four or six byte password to the packet. System cleaning software.Ether-wake needs a single dash ('-') in front of options. Innovative, hardware-accelerated terminal emulator
#Magic packet sender portable free
Learn Python with our recommended free books and free tutorials.Īll the essential tools in this series: Essential System Tools This consumes a very small amount of standby power. The only complexity is that it can take a little investigation to work out what changes are needed for each machine’s BIOS settings.Īnd remember that for WOL to work, parts of the network interface need to stay on. Even if your network has only two computers, it’s often convenient to be able to turn it on across the network. It’s not only useful for system administrators. GWakeOnLAN is a really simple and sweet utility. A system administrator can therefore turn on many computers across the network at the same time. We then need to click the box next to each machine we want to boot, and click the Turn on button. Our router holds this physical address for each computer on our local network. It is a 48 bit value, consisting of twelve hexadecimal characters. A MAC address is a unique physical address assigned to each network adapter in a computer.

We need to enter a name for the machine and its MAC address. To add another machine we click the green + button. The image shows we’ve set up three machines that we can wake up over the LAN. However, we have some systems which required a few changes in the Device Manager and the Control Panel. If the target machine is running Windows, generally there’s nothing needed to be done.

This command is required after each boot or we can make an appropriate change to the interfaces file. Where is the device name of your NIC, e.g. However, if the letter shown was d, the Magic Packet would not be enabled. We therefore don’t need to make any changes to the operating system. Here’s the output below from one of our systems.įor this particular system, the g tells us that the Magic Packet is already enabled. In Linux, this can be established with the ethtool utility. We need to ensure WOL is enabled in the NIC. It may also be necessary to configure the operating system of the target machine. We also need to set “Energy Efficient Ethernet” to OFF, and to set “Wake on Magic Packet” to Enabled. For example, with the HP EliteDesk 800 G2 Mini Desktop PC we need to enable boot to hard drive from the network. The precise steps depend on the BIOS of each target machine. There’s a few things we need to configure on each machine we want to wake up (we’ll call that the target machine).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
